Overview
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose) — an important source of fuel for your body.
With type 2 diabetes, your body either resists the effects of insulin — a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells — or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
Type 2 diabetes used to be known as adult-onset diabetes, but today more children are being diagnosed with the disorder, probably due to the rise in childhood obesity. There’s no cure for type 2 diabetes, but losing weight, eating well and exercising can help manage the disease. If diet and exercise aren’t enough to manage your blood sugar well, you may also need diabetes medications or insulin therapy.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. In fact, you can have type 2 diabetes for years and not know it. Look for:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Increased hunger
- Unintended weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you notice type 2 diabetes symptoms.
Causes
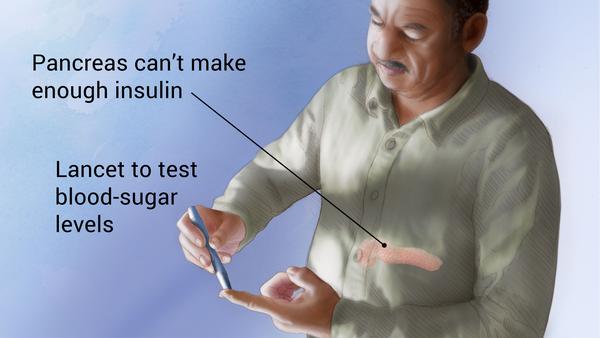
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin. Exactly why this happens is unknown, although genetics and environmental factors, such as being overweight and inactive, seem to be contributing factors.
How insulin works
Insulin is a hormone that comes from the gland situated behind and below the stomach (pancreas).
- The pancreas secretes insulin into the bloodstream.
- The insulin circulates, enabling sugar to enter your cells.
- Insulin lowers the amount of sugar in your bloodstream.
- As your blood sugar level drops, so does the secretion of insulin from your pancreas.
The role of glucose
Glucose — a sugar — is a main source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and other tissues.
- Glucose comes from two major sources: food and your liver.
- Sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it enters cells with the help of insulin.
- Your liver stores and makes glucose.
- When your glucose levels are low, such as when you haven’t eaten in a while, the liver breaks down stored glycogen into glucose to keep your glucose level within a normal range.
In type 2 diabetes, this process doesn’t work well. Instead of moving into your cells, sugar builds up in your bloodstream. As blood sugar levels increase, the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas release more insulin, but eventually these cells become impaired and can’t make enough insulin to meet the body’s demands.
In the much less common type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly destroys the beta cells, leaving the body with little to no insulin.
Risk factorsinsulin resistance.
Factors that may increase your risk of type 2 diabetes include:
- Weight. Being overweight is a main risk factor for type 2 diabetes. However, you don’t have to be overweight to develop type 2 diabetes.
- Fat distribution. If you store fat mainly in the abdomen, you have a greater risk of type 2 diabetes than if you store fat elsewhere, such as in your hips and thighs. Your risk of type 2 diabetes rises if you’re a man with a waist circumference above 40 inches (101.6 centimeters) or a woman with a waist that’s greater than 35 inches (88.9 centimeters).
- Inactivity. The less active you are, the greater your risk of type 2 diabetes. Physical activity helps you control your weight, uses up glucose as energy and makes your cells more sensitive to insulin.
- Family history. The risk of type 2 diabetes increases if your parent or sibling has type 2 diabetes.
- Race. Although it’s unclear why, people of certain races — including black, Hispanic, American Indian and Asian-American people — are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than white people are.s
- Age. The risk of type 2 diabetes increases as you get older, especially after age 45. That’s probably because people tend to exercise less, lose muscle mass and gain weight as they age. But type 2 diabetes is also increasing dramatically among children, adolescents and younger adults.
- Prediabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which your blood sugar level is higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Left untreated, prediabetes often progresses to type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes. If you developed gestational diabetes when you were pregnant, your risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases. If you gave birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds (4 kilograms), you’re also at risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome. For women, having polycystic ovarian syndrome — a common condition characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth and obesity — increases the risk of diabetes.
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck. This condition often indicate
Complications
Type 2 diabetes can be easy to ignore, especially in the early stages when you’re feeling fine. But diabetes affects many major organs, including your heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. Controlling your blood sugar levels can help prevent these complications.
Although long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually, they can eventually be disabling or even life-threatening. Some of the potential complications of diabetes include:
- Heart and blood vessel disease. Diabetes dramatically increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis).
-
Nerve damage (neuropathy). Excess sugar can cause tingling, numbness, burning or pain that usually begins at the tips of the toes or fingers and gradually spreads upward. Eventually, you may lose all sense of feeling in the affected limbs.
Damage to the nerves that control digestion can cause problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. For men, erectile dysfunction may be an issue.
- Kidney damage. Diabetes can sometimes lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- Eye damage. Diabetes increases the risk of serious eye diseases, such as cataracts and glaucoma, and may damage the blood vessels of the retina, potentially leading to blindness.
- Slow healing. Left untreated, cuts and blisters can become serious infections, which may heal poorly. Severe damage might require toe, foot or leg amputation.
- Hearing impairment. Hearing problems are more common in people with diabetes.
- Skin conditions. Diabetes may leave you more susceptible to skin problems, including bacterial and fungal infections.
- Sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea is common in people with type 2 diabetes. Obesity may be the main contributing factor to both conditions. Treating sleep apnea may lower your blood pressure and make you feel more rested, but it’s not clear whether it helps improve blood sugar control.
- Alzheimer’s disease. Type 2 diabetes seems to increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, though it’s not clear why. The worse your blood sugar control, the greater the risk appears to be.
Prevention
Healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent type 2 diabetes, and that’s true even if you have diabetes in your family. If you’ve already received a diagnosis of diabetes, you can use healthy lifestyle choices to help prevent complications. If you have prediabetes, lifestyle changes can slow or stop the progression to diabetes.
A healthy lifestyle includes:
- Eating healthy foods. Choose foods lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber. Focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Getting active. Aim for a minimum of 30 to 60 minutes of moderate physical activity — or 15 to 30 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity — on most days. Take a brisk daily walk. Ride a bike. Swim laps. If you can’t fit in a long workout, spread your activity throughout the day.others), an oral diabetes medication, may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. But even if you take medication, healthy lifestyle choices remain essential for preventing or managing diabetes.
- Losing weight. If you’re overweight, losing 5 to 10 percent of your body weight can reduce the risk of diabetes. To keep your weight in a healthy range, focus on permanent changes to your eating and exercise habits. Motivate yourself by remembering the benefits of losing weight, such as a healthier heart, more energy and improved self-esteem.
- Avoiding being sedentary for long periods. Sitting still for long periods can increase your risk of type 2 diabetes. Try to get up every 30 minutes and move around for at least a few minutes.
Sometimes medication is an option as well. Metformin (Glucophage, Glumetza,
